| Products > Waste Water Treatment (for ETP & STP ) > Membrane Based System>> |
|
| Membrane Bio Reactor(MBR):- |
 |
|
| |
| |
| |
| Introduction:- |
 |
|
| |
Membrane Bio Reactor (MBR) technique, a new method for wastewater treatment, integrates membrane separation and biotechnology, rejects activated sludge and macromolecular organic matter in aerobic tank/MBR tank with membrane separation plant, thus saving the use of secondary sedimentation tank. Consequently, the concentration of activated sludge rises greatly, the HRT and the SRT could be controlled separately, and difficult degraded matters are constantly degraded and reacting in reactor. Therefore, compared to traditional biological treatment methods, MBR technique greatly strengthens the function of the bioreactor with the using of membrane separation. Fig. shows the typical MBR concept of combination of Activated sludge process and membrane filtration. |
| |
|
| |
| Fig. Typical MBR concept of combination of Activated sludge process and membrane filtration. |
| |
| Basic Structure :- |
 |
|
| |
SHIVAM offers two type of Membrane Bio-reactor system.
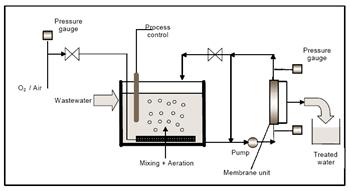
(1) Pressure driven(Side-stream filtration):
- In-pipe cartridge systems that are located external to the bioreactor.
- More prevalent in industrials systems where waste characteristics, such as high temperatures, require the use of ceramic membranes.
|
| |
|
| |
| Pressure Driven MBR Layout |
| |
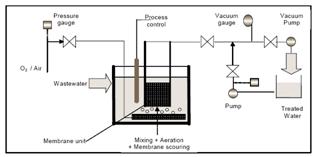
(2) Vacuum driven (Submerged filtration):
- Immersed systems that are designed for installation within the bioreactor.
- Using hollow-fibre or flat-sheet membranes are most important in MBR application because they operate at lower operating pressure or vacuums.
- More readily accommodate the variations in types of solids found in activated sludge bioreactors, typically provide a lower life-cycle cost, particularly for municipal scale facilities.
- An immersed membrane bioreactor system can combine the function of an activated sludge aeration system, secondary clarifier, and tertiary filtration in a single tank.
|
| |
|
| |
| Vacuum Driven MBR Layout |
| |
Salient Features of MBR:-
- MBR produce extremely good quality filtered water with less than 1 NTU turbidity and less than 10 mg/L O2 BOD consistently.
- MBR improves effectiveness of biological process by allowing it to operate at high solids concentration and eliminating problem such as sludge bulking, sludge rising, nocardia Foam etc
- MBR reduces biological treatment plant size and produces less sludge.
- When used before RO, MBR eliminates need for secondary and tertiary treatment equipment. In spite of this, the filtered water quality is acceptable to RO which operates smoothly.
- Single package unit with minimum civil construction
- Modular in construction & design
- Compact requires 25% of a convectional system
- Low energy consumption (1.14 kwh/1000gal)
- Filtration Up to 6 log (99.999%) removal of total coli form
- No chemical required during treatment
|
| |
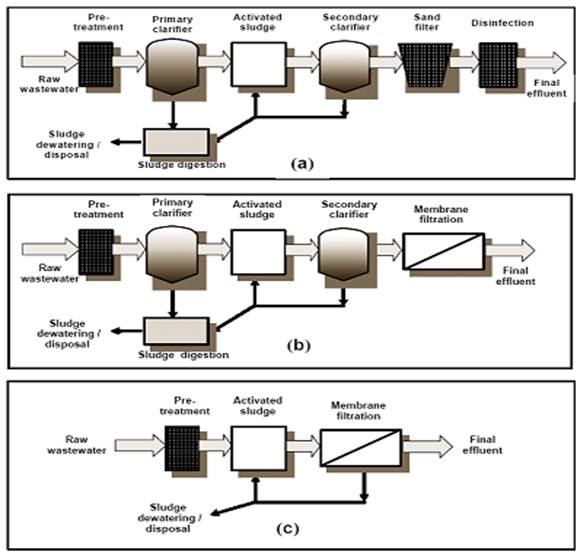
Process Comparison Of MBR With Conventional Treatment Train:-
MBR can be placed in the existing and new wastewater treatment/sewage treatment plant as indicated in the figures below.
Fig.(a) shows the simple treatment train take place in sewage treatment / wastewater treatment plants.
Fig.(b) shows how membrane filtration can take place in the existing plant, which eliminates the need of tertiary treatment and ensure the product water quality < 1 NTU.
Fig.(c) shows the typical treatment train, which eliminates the need of secondary treatment , tertiary treatment need and consistently gives water with <1 NTU need. |
| |
|
| |
| Process comparison of MBR with conventional treatment |
| |
| Technical Comparison - Conventional Asp Vs. Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) Design Parameters |
| |
PARAMETERS |
ASP |
MBR |
Flow, m3/d |
1000 |
1000 |
Aeration Tank Volume, m3 |
780 |
170 |
Clarifier Volume, m3 |
100 |
NA |
Power Requirement, HP |
55 |
10 |
Land Requirement, m2 |
350 |
100 |
|
| |
| Quality Comparison |
| |
PARAMETERS |
ASP |
MBR |
PH |
6.5 – 8.5 |
6.5 – 8.5 |
BOD, ppm |
< 30 |
< 5 |
COD, ppm |
< 100 |
< 20 |
TSS, ppm |
< 100 |
< 5 |
|
| |
Applications:- |
 |
|
| |
- Need to recycle high quality water
- Need to upgrade old plant
- Where space is limited
- Need to preserve appearance of a clean/ tourist area(hospitals, hotels, malls)
- Housing complex
- Hotels & Township
- Golf & Country Club
- Industrial Estates
- Industrial waste treatment
- Waste recycle
- Existing plant upgrade/ capacity expansion
- RO Pretreatment of sea water and brackish waters
- Add on for industrial biological processes for high quality
- Permeate and higher performance
- Vacuum Driven (Submerged filtration)
|
| |
Advantages:- |
 |
|
| |
Membrane bioreactors are effectively used to treat both municipal and industrial wastewater, and some of these are listed below:
- Exceptional effluent quality
- Biomass completely retained, result in consistently high-quality final effluent, effluent quality solids concentrations are <1 mg/L (<1 ppm).
- Compared to conventional activated sludge plants with clarifier, the effluent quality is less dependent on the mixed liquor suspended solids(MLSS) concentration and sludge settling properties(Sludge Volume Index).
- Small Footprint
- Secondary clarifiers and effluent filters can be eliminated, thereby reducing plant footprint area.
- Because elevated mixed liquor concentrations are possible, the aeration basin volume can be reduced, further reducing plant footprint.
- Long solids retention times (SRTs) can be achieved in a small footprint; result is sludge production equivalent to an extended aeration system on less land than an equivalent Conventional Activated Sludge (CAS) plant.
- Modular system
- Membrane systems are modular in nature, allowing for ease of expansion, and flexible in configuration, making them a popular option for plants looking to retrofit older technology.
- Robust and reliable operation
- System can operate within a wide range of SRTs, resulting in increased flexibility and more options for system optimization.
- System is robust enough to handle elevated MLSS concentrations for short periods of time, allowing for flexible solids wasting schedules.
- Processes are easily automated; operator requirements are reduced, consisting that operators are not required to closely manage sludge settling issues.
- Reduced downstream disinfection requirements
- A physical mechanism to remove pathogens is provided.
- Low-turbidity effluent reduces downstream disinfection requirements; high transmissivity means less energy required for UV disinfection; effluent has minimal chlorine demand, so less is required to achieve the target residual concentration.
- Compact systems significantly reducing plant footprint.
|
| |
| |